
Antibacterial Operating Room
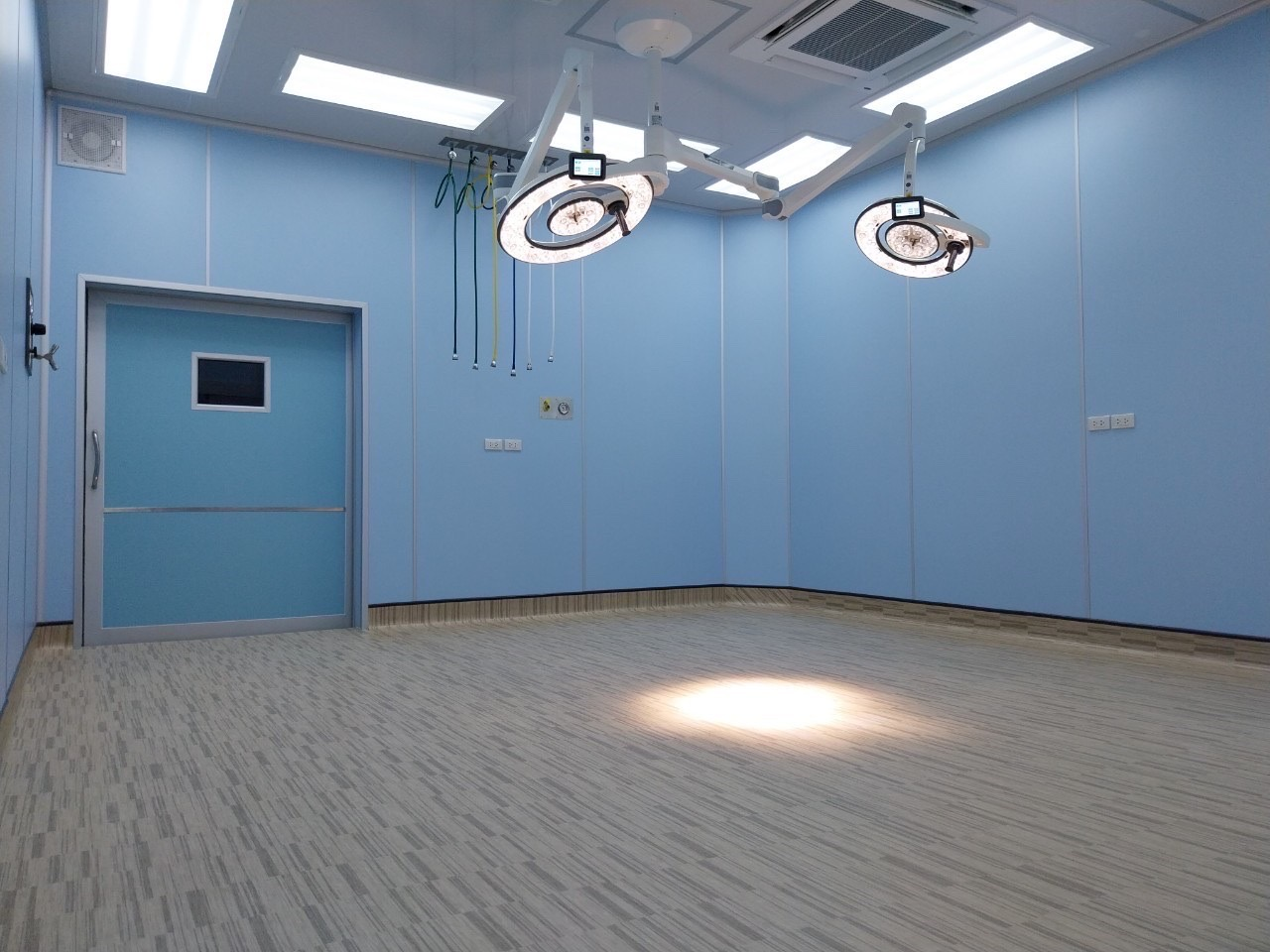
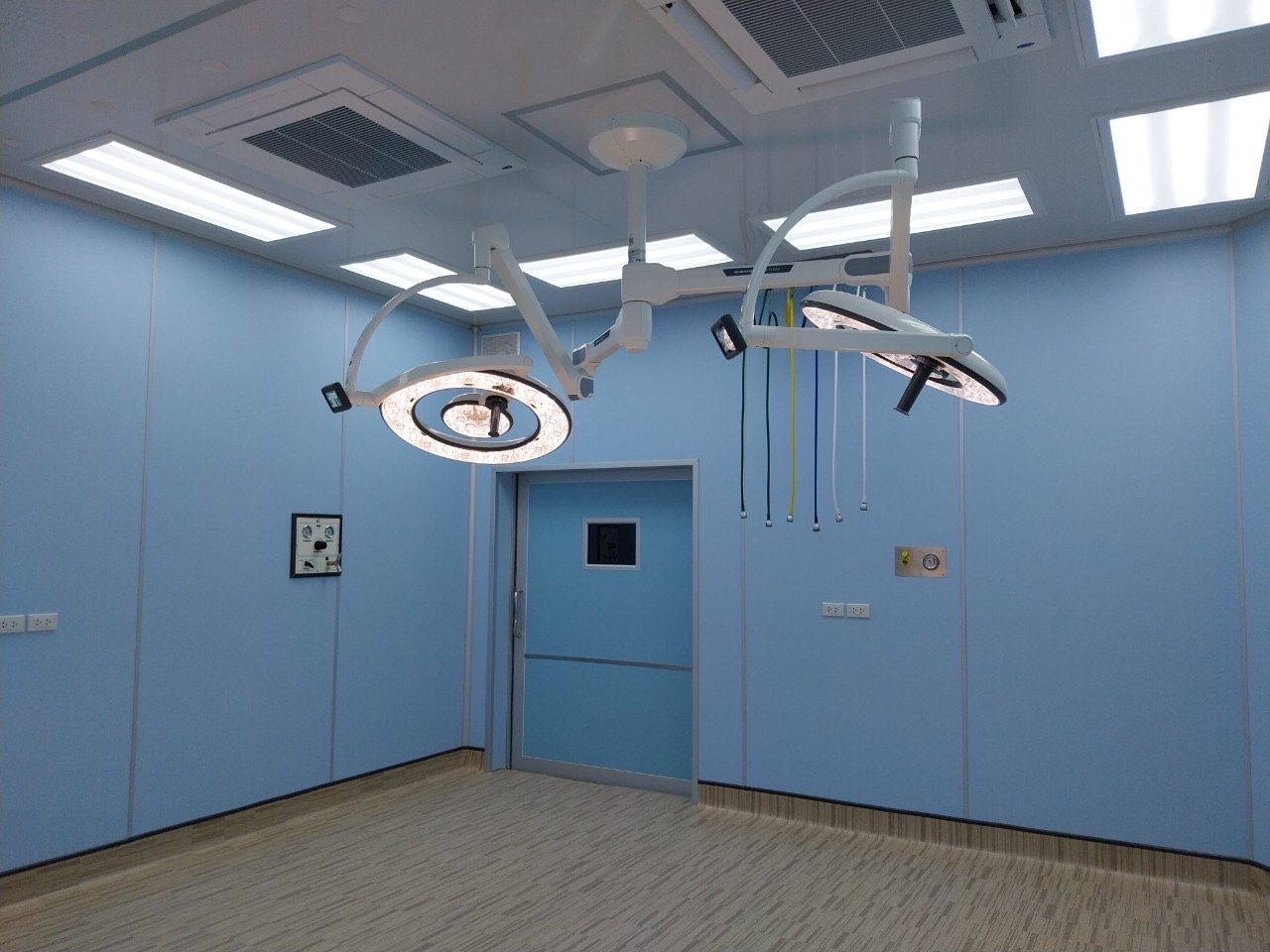
An antibacterial operating room (AOR) is a surgical suite designed to minimize the presence of bacteria and other microorganisms. The goal of an AOR is to reduce the risk of surgical site infections (SSIs), which are infections that occur in the incision site after surgery.
AORs incorporate a number of features that go beyond those of a standard operating room, including:
Design:
- Air filtration systems: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters are used to remove dust and microorganisms from the air.
- Air pressure: The air pressure in the AOR is kept higher than the surrounding area to prevent air from flowing in from outside.
- Airflow: Air is circulated in a unidirectional flow, from the ceiling to the floor, to prevent the spread of contaminants throughout the room.
- Surfaces: Surfaces are made of smooth, easy-to-clean materials that are resistant to disinfectants.
Benefits of AORs:
- Reduced risk of SSIs
- Faster patient recovery
- Shorter hospital stays
- Lower healthcare costs
AORs are becoming increasingly common for certain types of surgery, particularly those that are at high risk of infection, such as joint replacement, heart surgery, and organ transplants.


Related Content
ห้องผ่าตัดระบบความดันลบ (Negative pressure) ที่โรงพยาบาลปัตตานี








